Filter events in a Grepr pipeline
You can use filter transforms in a Grepr pipeline to include or exclude log events based on specific conditions. Filters are configured using familiar query interfaces, such as SQL or Datadog, SPL, and New Relic-like query syntaxes.
The filtering configuration options allow you to create simple to complex event routing scenarios, including selective application of transformations to a subset of events or routing different types of events to appropriate processing stages using flexible configuration options.
Filtering options
The following is a summary of the options available when configuring filters in a Grepr pipeline:
- Drop late-arriving events.
- Pass all or only some events to the next step.
- Process all or only some events using SQL before passing to a configurable pipeline step.
- Pass all records to the next pipeline step and also through the SQL processing path.
Drop late-arriving data
You can configure a maximum threshold for the difference between the event and received timestamps. The threshold is configured using a duration in the ISO-8601 format. Events that exceed this threshold are dropped from the pipeline. This is useful for scenarios where timely data is critical, and late-arriving events could affect analysis or reporting.
Pass events to the next pipeline step
You can configure filters to pass events to the next step in the pipeline. You can pass all events through to the next pipeline step, use a filter query to pass only events that meet specific conditions, or disable the passthrough of events with the option of passing the events for SQL processing.
Filter queries use familiar query syntax similar to that of popular observability platforms, such as Datadog, Splunk, and New Relic. To learn more about the supported query syntaxes, see Query log data in Grepr.
Process events with SQL
The SQL processing path allows you to define complex transformations using ANSI standard SQL queries. You define the SQL query to process events and the name of a view to contain the results of query processing. You can create multiple queries and views that process data sequentially, with each view able to reference input events through the logs input table or previously defined views. Based on the filter’s location in the pipeline, the results of SQL processing can be routed to specific pipeline steps, such as the JSON or Grok parsers, the Data Lake, the Reducer, or directly to the pipeline Sinks.
You can choose to process all events or only events that don’t meet the criteria for passthrough to the next pipeline step. You can further select specific events for SQL processing using a filter query. This feature provides flexibility to apply SQL transformations only to relevant events.
You can also choose to materialize the results of query processing for reuse in subsequent views, improving performance for complex transformation scenarios.
When you transform events using SQL, the results of processing replace the original event. If you want to retain all fields from the original event, include the wildcard character (*) in your SELECT statement. For example, to transform the severity while keeping all other fields: SELECT *, CASE WHEN severity > 16 THEN 21 ELSE severity END as severity FROM logs.
To learn more about using SQL in Grepr pipelines, see Transform events with SQL.
Configure filters in the Grepr pipelines UI
In the Grepr pipelines UI, filters are available in predefined locations in a pipeline. To add one of these filters to your pipeline:
-
In the Grepr pipelines UI, in the left-hand navigation menu, select the Pre-parsing, Post-parsing, or Post-warehouse filter to open the filter detail pane.
-
In the filter detail pane, click the pencil icon to display the filter configuration form.
-
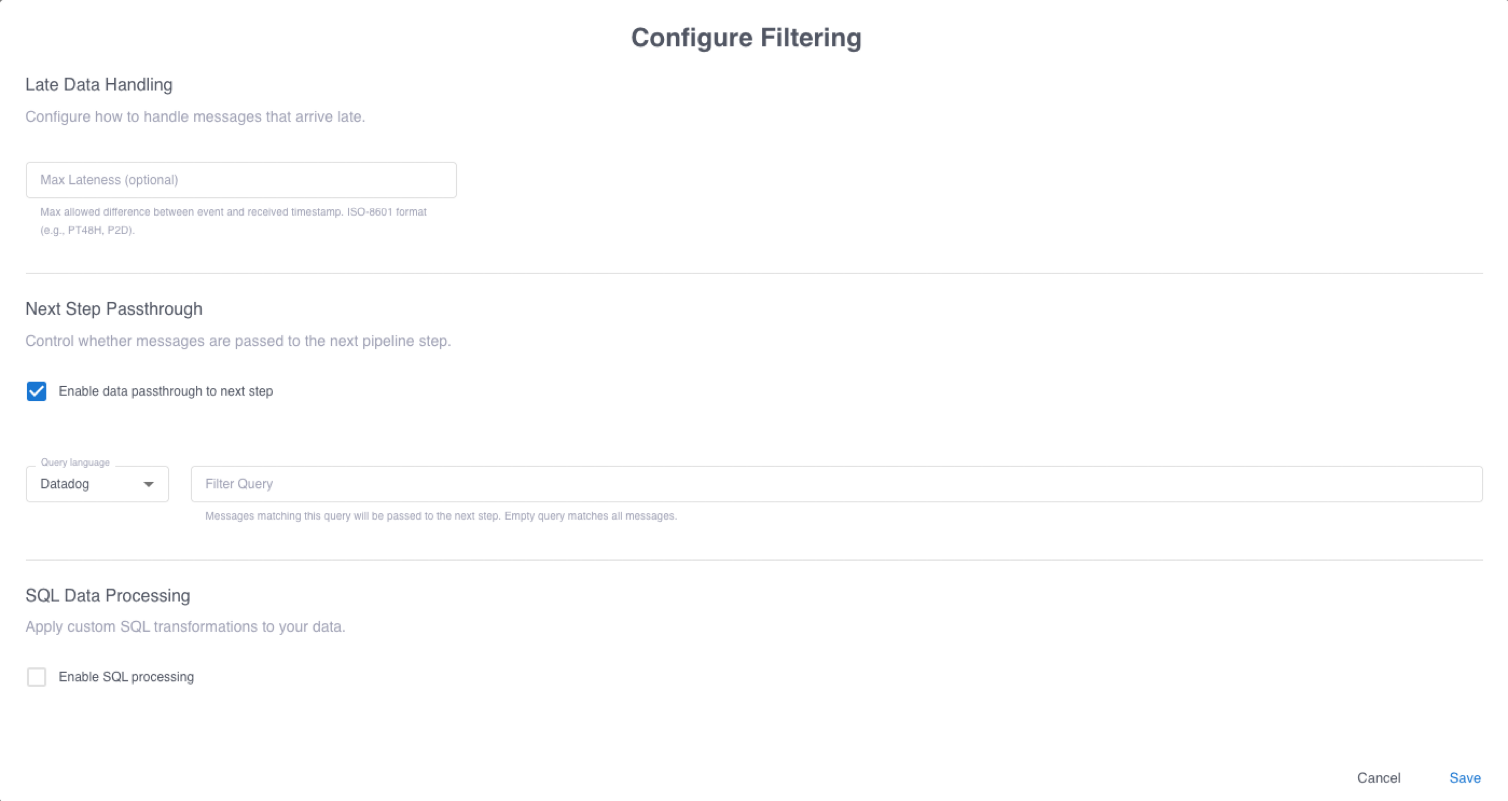
Configure the filtering and routing of events:
- In the Max Lateness field, optionally enter a duration in ISO-8601 format to drop late-arriving data.
- In the Next Step Passthrough section, to pass events to the next pipeline step, ensure that Enable data passthrough to next step is selected. To optionally select events for passthrough based on specific criteria, enter a query in the Filter Query field.
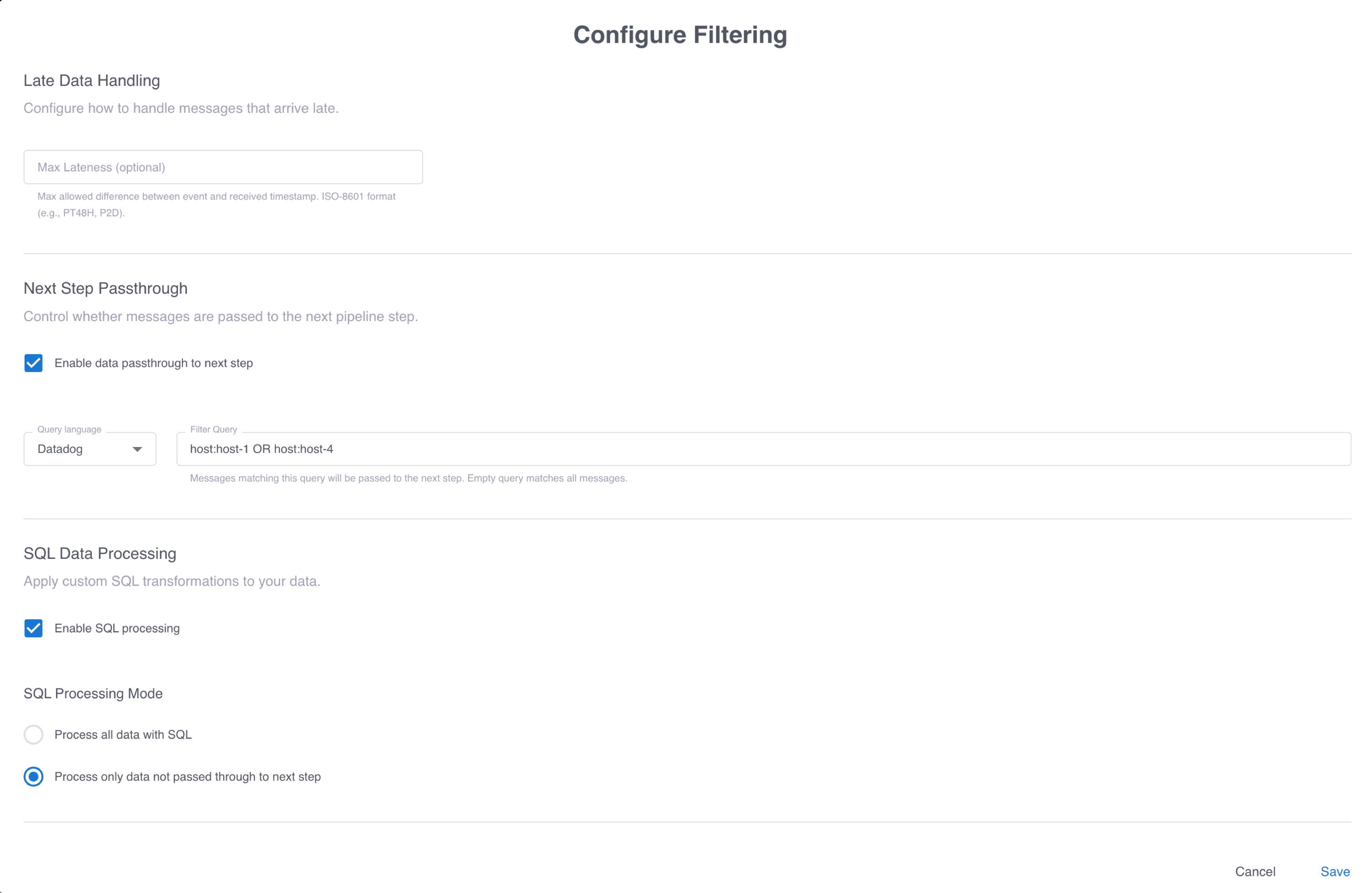
- To process events using SQL, select Enable SQL processing and select whether to process all events or only events that are not passed to the next step. Optionally enter a query in the Filter Query field to conditionally select events for SQL processing. This screenshot shows a filter configuration that passes events associated with
host-1andhost-4to the next pipeline step. All other events are processed using SQL.
-
Configure how to process events with SQL:
- To optionally apply SQL processing to events that meet specific criteria, enter a query in the SQL Filter Query field.
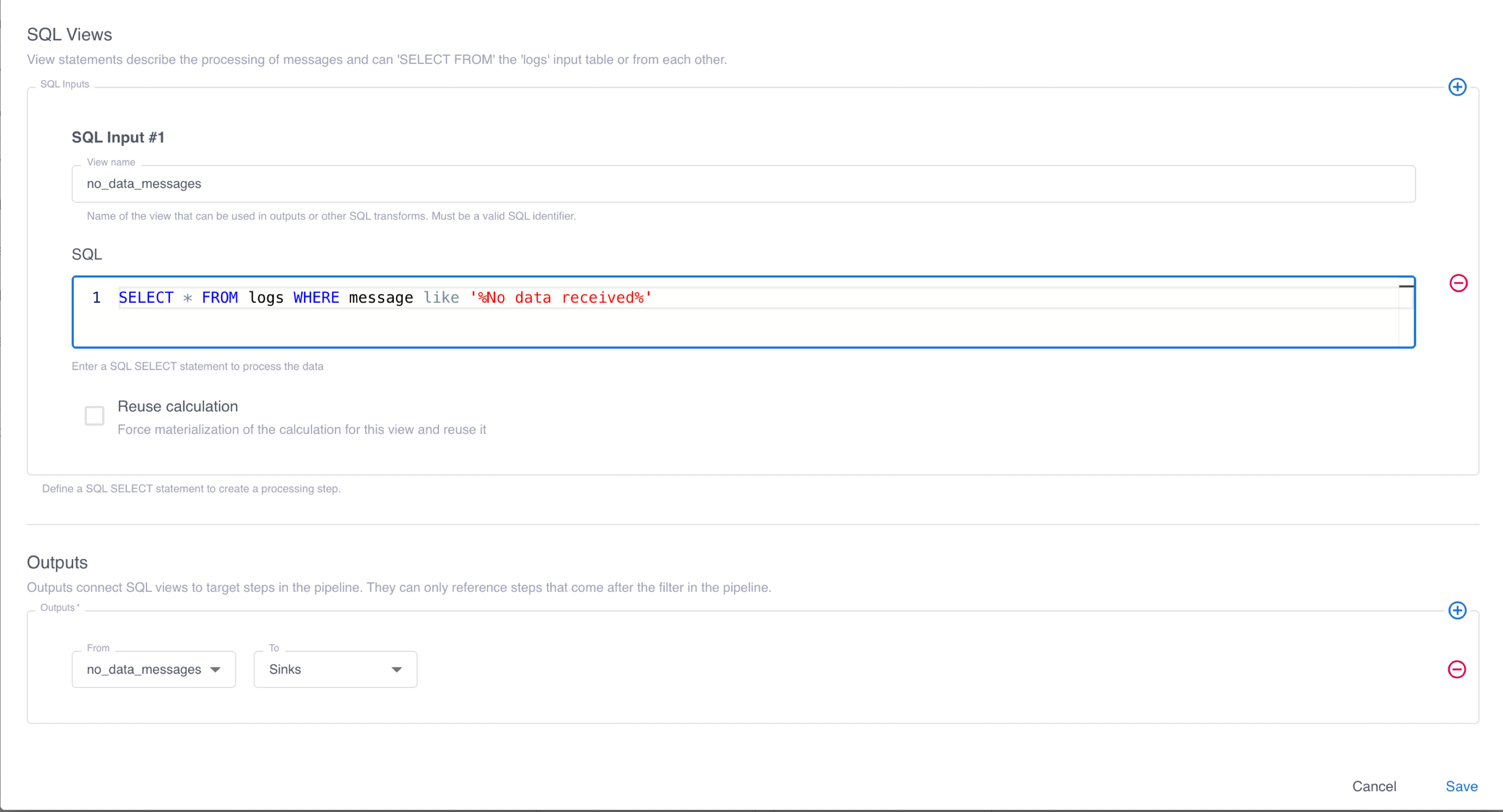
- In the SQL Views section, click the plus sign to add one or more SQL Input definitions. In the View name field, enter a name for the view to contain the results of processing, and in the SQL field, enter the SQL query to process input events.
- Optionally select Reuse calculation to materialize the results of query processing for reuse in subsequent views.
- In the Outputs section, configure one or more pipeline steps to receive the results of SQL processing. This screenshot shows a configuration that selects events where the message includes
No data receivedand saves them to a view namedno_data_messages. The view is then routed to the pipeline sinks, which forward it to your observability platform or other destinations.